When you start to build your building, many technical or engineering questions arise that you must solve, one of these questions is: What capacity of elevators to choose?
At that moment you find that all the elevator companies ask you about (stops, capacity, dimensions of the gap among others), in the end you end up overwhelmed without having a clear path to start.
Therefore, it is very important that before you have received any calls or if you have already contacted you, you know which elevator is the right one for your building.
The methodology that we are going to use is the one used by Gina Barney and Richard Peters, their analysis is based on the amount of upward traffic in the building, that is, to provide an efficient solution for the number of people who need to be transported in a time range of 5 minutes in the elevator.
Therefore, the equation that you will have to solve is: The elevator solution (s) you choose should transport without any inconvenience the population of people who would arrive at the building in a time range of 5 minutes.
Main Formula
HC5 = %POP
* %POP: It is the demand of passengers who arrive at the building in a time of 5 minutes.
Elevator solution calculation (HC5) in a time of 5 minutes (300 seconds)
HC5 = 300xP / RTT : Solution for one (1) elevator.
HC5 = 300xPxL / RTT : Solution for more than one (1) elevator or group of elevators.
Calculation of travel time (RTT) from main stop
HC5= 300 x P X L / (2Htv + (S+1)ts + 2Ptp)
RTT = 2Htv + (S +`1) ts + 2Ptp
*tv: It is the average speed of the elevator measured in (m / s).
*S: It is the probable number of stops.
*ts: It is the time consumed in stops.
*P: It is the average number of passengers in the elevator. It should be noted that P appears in the numerator and denominator of the equation.
* tp: It is the average time it takes for the elevator to transfer people.
Calculation of the waiting time from the departure of an elevator to the arrival of another elevator, only for a group of elevators.
INT= RTT / L
Simplified International Standard
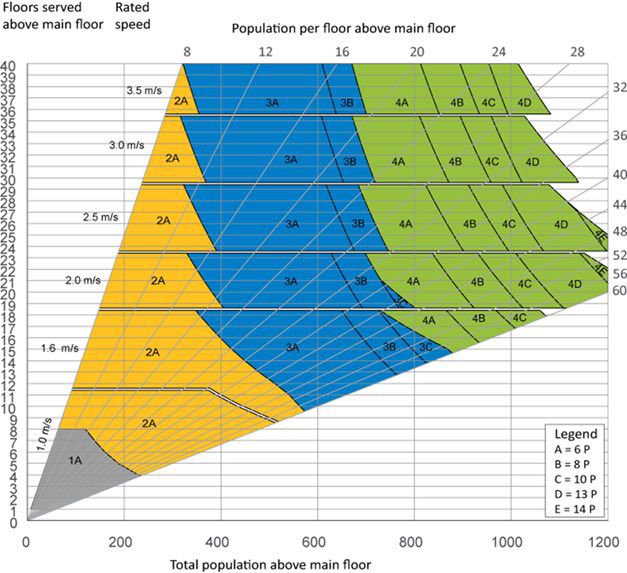
The following graph shows the relationship of the amount of population of a project vs the number of stops, on the horizontal axis we find the total population of the building measured in people (X) on the vertical axis we find the number of stops of the project above the main floor or floor 0 (Y).
This graph also shows us the recommended elevator speed for each type of need, taking into account the population of a building and the number of stops. For example, we see that the speed of 1 m / s and one (1) elevator solves the needs of buildings with populations between 1 - 225 people and 1 - 8 stops above the main stop (without basements).
The 4 steps to define the capacity of your elevator in 15 minutes.
Learn how to define the capacity of your lift
Ascensores Camilleros Equipo nuevo